Blog | nearby computing
Assessing Your Digital Transformation Progress: Where Does Your Company Stand on the Edge Adoption Maturity Scale?
What is Digital Transformation Maturity Model?
Digital transformation maturity model entails the seamless integration of digital technology throughout every facet of a business, fundamentally altering the way operations are conducted and value is delivered to customers. This is a multifaceted and intricate undertaking, necessitating a shift in company culture and a new perspective on its significance. It is not a one-time system upgrade but instead an ongoing journey involving continuous innovation, oversight, and feedback.
Digital transformation has assumed a significant role in reshaping enterprises and aligning them with an interconnected industry. This process demands a heightened level of individual awareness and cohesively brings together all aspects of a company. Nowadays, businesses are harnessing cutting-edge technologies to transition from mass production to more personalized manufacturing approaches.
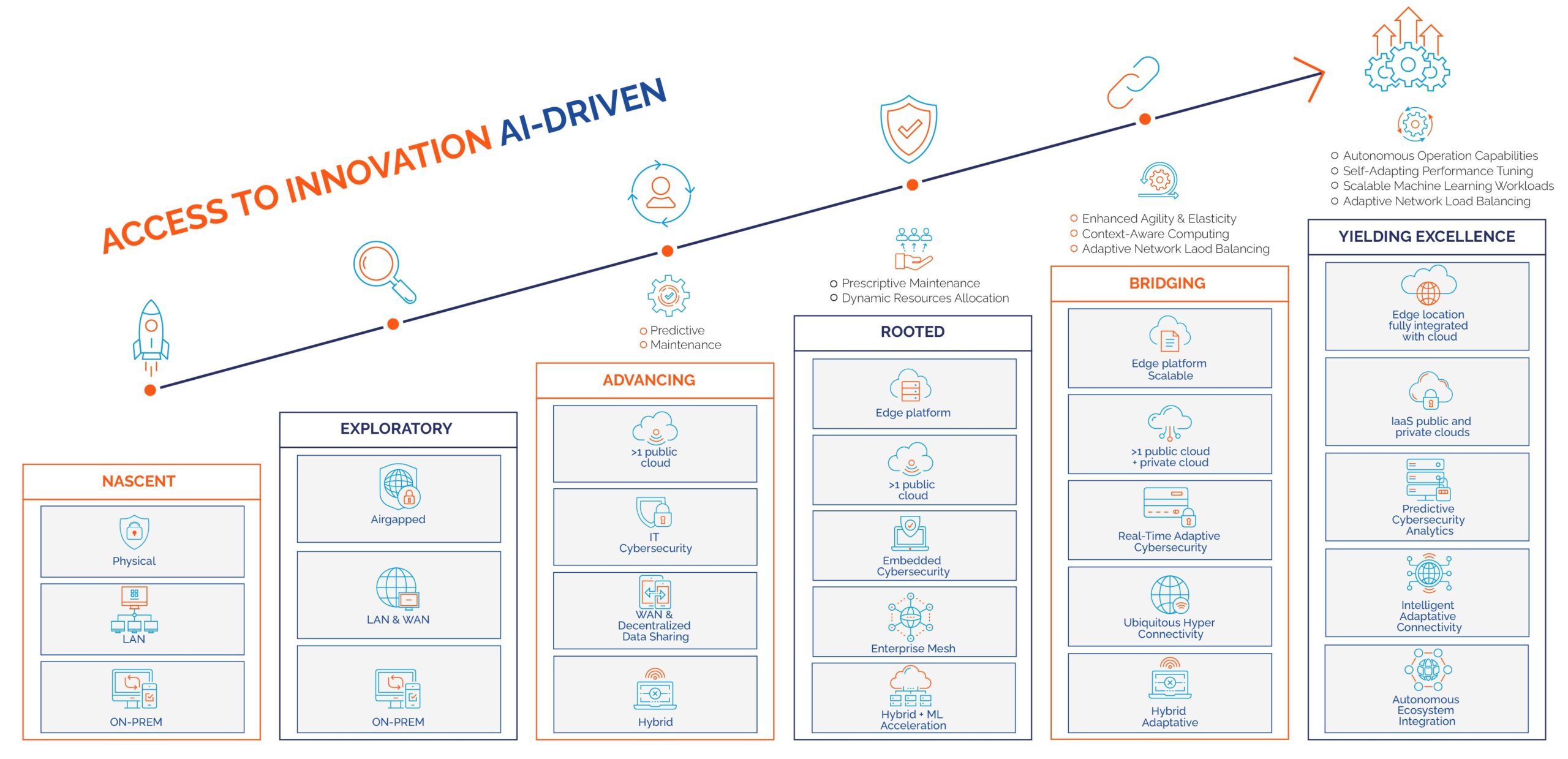
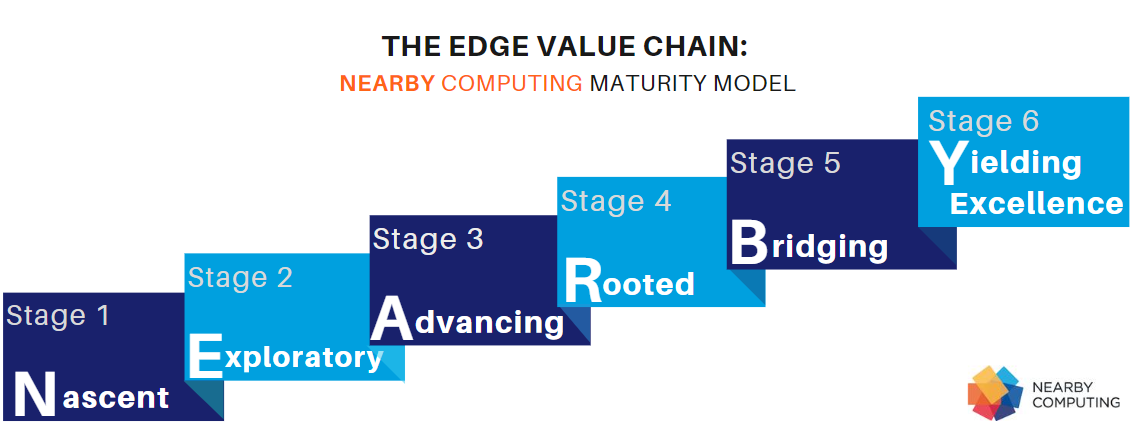
Nearby Computing has established a framework called “NEARBY” consisting of six maturity levels for edge adoption, offering businesses a clear gauge of their progress in achieving digital transformation.
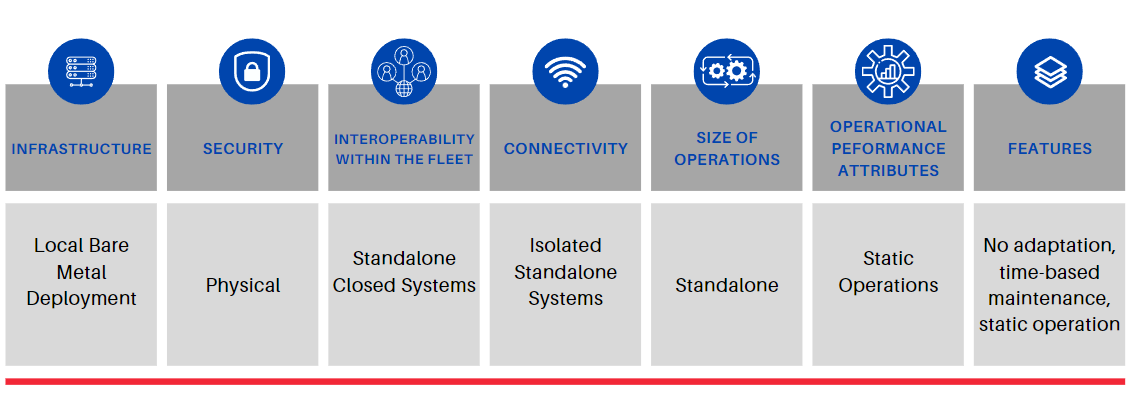
Stage 1. Nascent.
At this initial stage of the digital transformation maturity model, companies are in the early stages of delving into the possibilities of technology. They may have basic IT infrastructure in place, but a well-defined strategic direction is lacking. Decision-making is typically ad hoc, and there is little to no formalized approach to technology adoption.
Cloud adoption: Companies at this stage use on-prem setups and have not adopted cloud services and rely solely on on-premises data centers and infrastructure. Their understanding of cloud benefits and strategies is minimal or non-existent.
Edge adoption: Companies at this stage are Uninitiated and have not adopted any edge computing solutions. Their operations are centred around traditional centralized data centers, and they might be unaware or only have basic knowledge of the benefits and potential of edge computing.
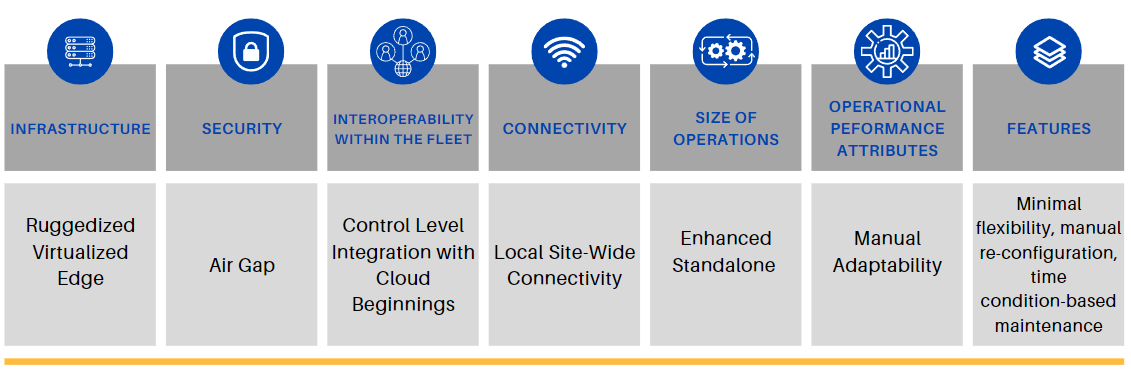
Stage 2. Exploratory.
Organizations at this stage are beginning to acknowledge the importance of technology but are still in the initial phases of its integration. There is a growing awareness of industry trends, and they make initial investments in technology to address immediate business requirements.
Cloud adoption: Organizations at this stage is exploring and has some level of Cloud Awareness and have started to recognize the potential of cloud technologies. They might be researching cloud vendors, understanding cost benefits, or experimenting with a few cloud-based applications, but haven’t committed to significant migrations or deployments.
Edge adoption: Organizations at this stage are Aware and recognize the potential benefits of edge computing but have not yet deployed any edge solutions. They might be in the process of researching suitable technologies, identifying use cases, or even experimenting with initial pilot projects.
Stage 3. Advancing.
At this point of the digital transformation maturity model, companies have initiated the development of a more defined technology strategy. They have established dedicated IT teams, adopted a more structured approach to technology adoption, and are actively searching for opportunities to use technology to achieve their business objectives. Additionally, they may begin experimenting with advanced technologies, although typically on a limited scale.
Cloud adoption: At this stage, companies are in a transitional level with Partial Migration and has moved some of their workloads or applications to the cloud. They might be leveraging Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or Platform as a Service (PaaS) but haven’t fully integrated cloud into their IT strategy. There’s an increased understanding of the cloud, but it’s not yet at the core of their operations.
Edge adoption: At this stage, companies have some Tentative Deployments and have launched limited edge computing projects, often in a controlled or pilot environment. The deployments are not widespread, but there’s a clear intention to learn and understand edge dynamics better.
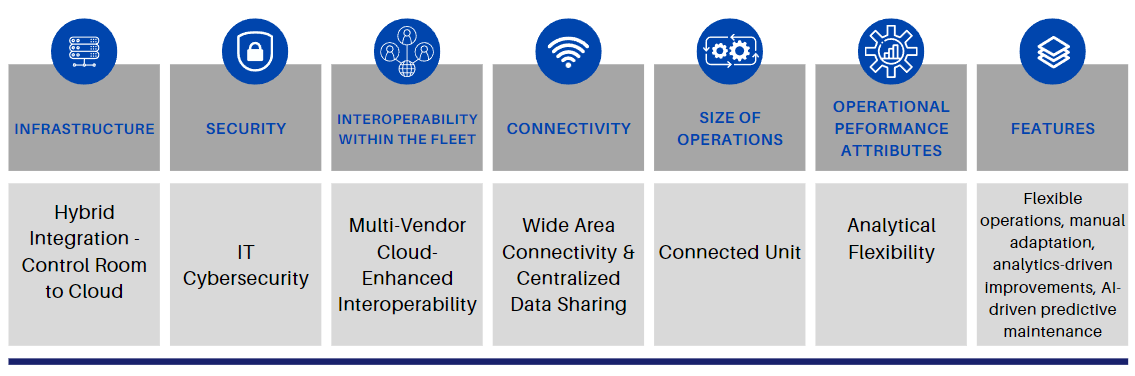
Stage 4. Rooted.
At this stage of the digital transformation maturity model, technology has evolved from being merely an add-on to becoming an integral component of business processes. Companies have a clearly defined tech strategy, and there is a robust alignment between business objectives and IT goals. Advanced technologies are being piloted and adopted across various departments.
Cloud adoption: Organizations here are Operational with having adopted a ‘Cloud-First’ approach, prioritizing cloud solutions over traditional on-premise options. They might be leveraging multiple cloud services, including Software as a Service (SaaS), IaaS, and PaaS. They have a well-established cloud strategy, with a majority of their workloads running in the cloud.
Edge adoption: Companies at this stage of the digital transformation maturity model, have reached Operational Integration and has started to integrate edge computing into their regular operations. Multiple projects or use cases are running on edge platforms. There’s a strategy in place to guide the scaling and deployment of edge solutions.
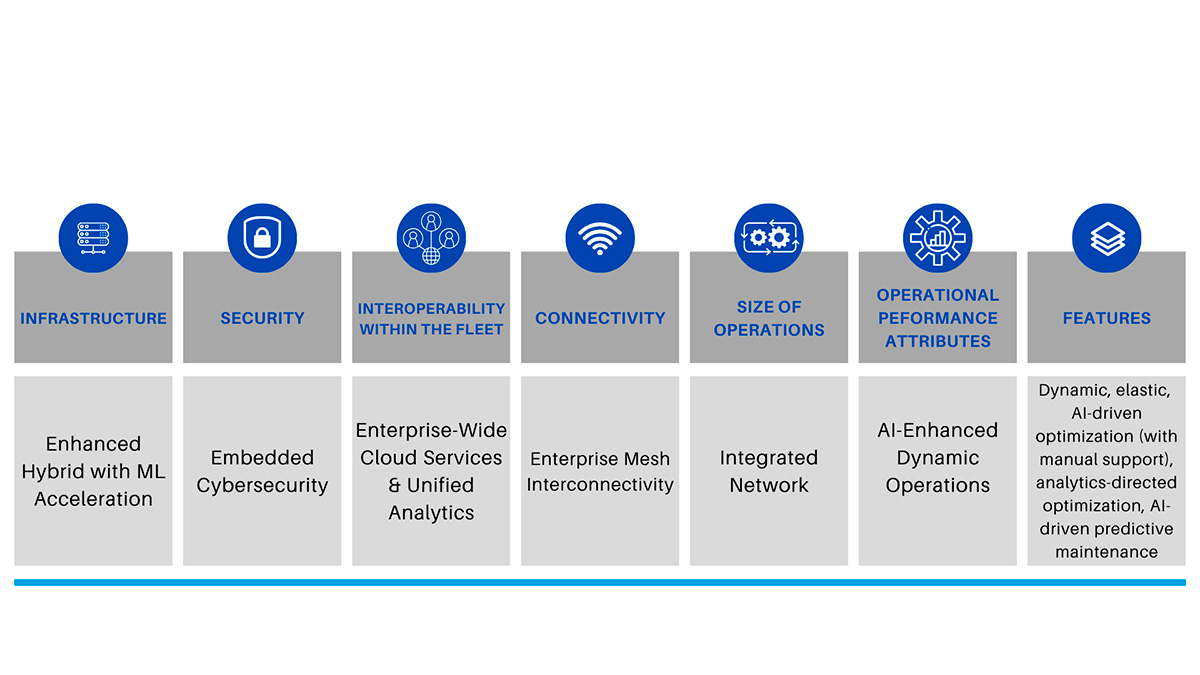
Stage 5. Bridging.
At this advanced level, companies are using technology not only for enhancing efficiency but also for fostering innovation and gaining competitive advantages. There’s an ongoing and proactive process of evaluating technology, and investments are made with foresight rather than reactively. The organization demonstrates agility and can swiftly adapt to evolving tech trends.
Cloud adoption: Companies at this stage are strategic with mulit-cloud adoption, utilizing more than one cloud service provider, ensuring redundancy, flexibility, and optimization. They understand the nuances between different cloud providers and select services based on suitability rather than convenience. Their strategy ensures risk diversification and maximizes cloud capabilities.
Edge adoption: Organizations have a Robust and Scalable edge computing framework that allows for scalable deployments. They can quickly launch and manage new edge projects. They have also addressed challenges like security, data management, and integration with centralized systems.
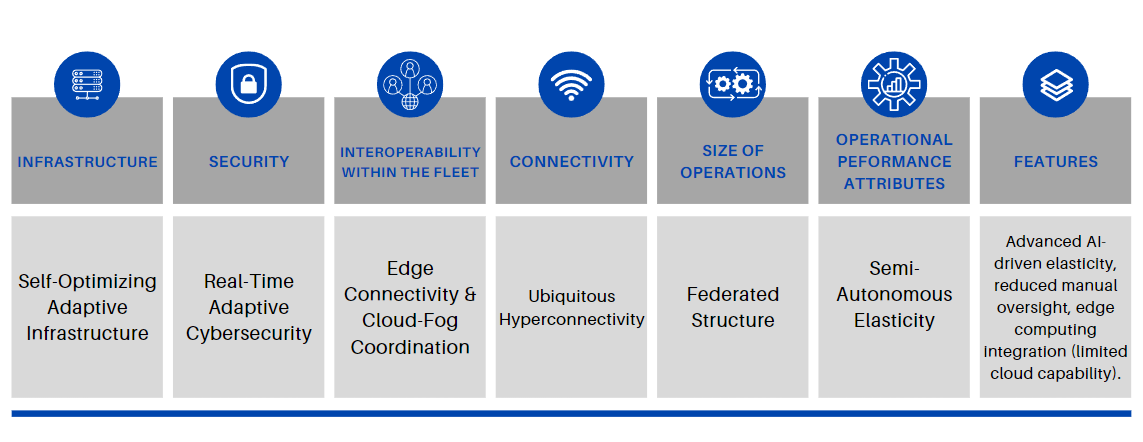
Stage 6. Yielding Excellence.
At this stage, companies are beginning to formulate a more defined technology strategy. They have established dedicated IT teams, adopted a more structured approach to technology adoption, and are actively exploring opportunities to utilize technology to meet their business objectives. Additionally, they may initiate limited-scale experiments with advanced technologies.
Cloud adoption: At this stage, companies are in a transitional level with Partial Migration and has moved some of their workloads or applications to the cloud. They might be leveraging Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or Platform as a Service (PaaS) but haven’t fully integrated cloud into their IT strategy. There’s an increased understanding of the cloud, but it’s not yet at the core of their operations.
Edge adoption: Advanced AI-driven elasticity, reduced manual oversight, edge computing integration (limited cloud capability).
By partnering with Nearby Computing, you can unlock the full potential of you digital transformation. With NearbyOne we can help companies to reach all opportunities in any stage of the digital transformation maturity model.